1846. Maximum Element After Decreasing and Rearranging
1) 문제 설명
You are given an array of positive integers arr. Perform some operations (possibly none) on arr so that it satisfies these conditions:
- The value of the first element in arr must be 1.
- The absolute difference between any 2 adjacent elements must be less than or equal to 1. In other words, abs(arr[i] - arr[i - 1]) <= 1 for each i where 1 <= i < arr.length (0-indexed). abs(x) is the absolute value of x.
There are 2 types of operations that you can perform any number of times:
- Decrease the value of any element of arr to a smaller positive integer.
- Rearrange the elements of arr to be in any order.
Return the maximum possible value of an element in arr after performing the operations to satisfy the conditions.
Example 1:
Input: arr = [2,2,1,2,1]
Output: 2
Explanation:
We can satisfy the conditions by rearranging arr so it becomes [1,2,2,2,1].
The largest element in arr is 2.
Example 2:
Input: arr = [100,1,1000]
Output: 3
Explanation:
One possible way to satisfy the conditions is by doing the following:
1. Rearrange arr so it becomes [1,100,1000].
2. Decrease the value of the second element to 2.
3. Decrease the value of the third element to 3.
Now arr = [1,2,3], which satisfies the conditions.
The largest element in arr is 3.
Example 3:
Input: arr = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: 5
Explanation: The array already satisfies the conditions, and the largest element is 5.2) 제한 사항
- 1 <= arr.length <= 105
- 1 <= arr[i] <= 109
3) 도전 과제
X
4) 풀이
Arrays.sort를 이용해 오름차순으로 정렬한 다음, 첫 값을 1로 두고 값을 천천히 올린 후 배열의 마지막 값을 가져왔다.
문제에 다른 의도가 있는 건지, 아니면 정렬을 직접 구현하도록 한 건지는 잘 모르겠다.
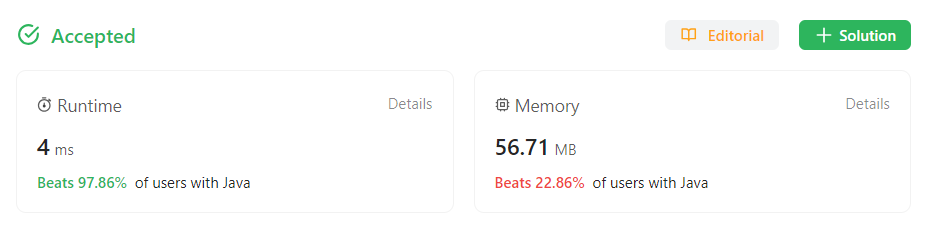
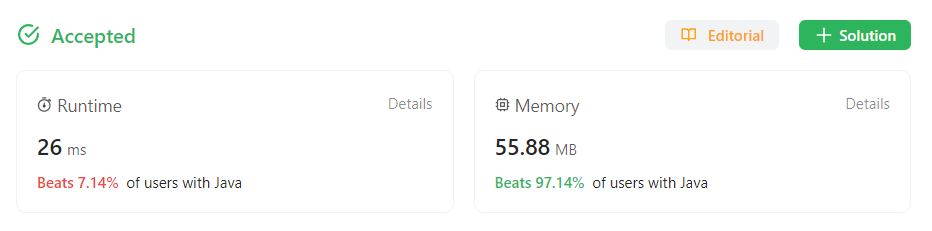
Arrays.sort를 이용해서 그런지 메모리 사용률이 굉장히 높게 나왔다. 아마 java에서 sort를 할 때 배열을 계속 복제해야 하다 보니 메모리 사용률이 높은 것으로 보인다. List로 바꾼 후 정렬하는 게 오히려 더 빠를 수도?? => 1mb 미만의 차이로 상대적인 메모리 사용량이 22.78에서 97퍼까지 오른다. 메모리는 신경쓰지 말자. 덤으로 리스트보다 배열이 압도적으로 빠르다.
5) 소스 코드 및 결과
import java.util.Arrays;
class Solution {
public int maximumElementAfterDecrementingAndRearranging(int[] arr) {
Arrays.sort(arr);
arr[0] = 1;
for(int i=0; i<arr.length-1; i++){
if(arr[i+1] == arr[i]){
continue;
}
arr[i+1] = arr[i]+1;
}
return arr[arr.length-1];
}
}
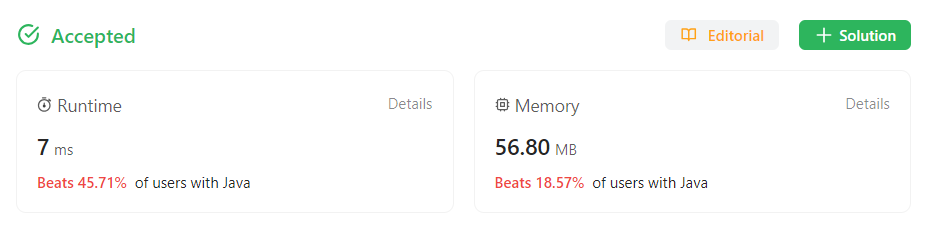
6) 다른 사람의 풀이
class Solution {
public int maximumElementAfterDecrementingAndRearranging(int[] arr) {
Arrays.sort(arr);
arr[0] = 1; // first condition
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; ++i) {
if (Math.abs(arr[i] - arr[i - 1]) <= 1) {
continue; // purposely wrote for understanding
} else {
arr[i] = arr[i - 1] + 1; // second condition
}
}
return arr[arr.length - 1];
}
}
'알고리즘 풀이' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 231209 LeetCode 문제 풀이 (0) | 2023.12.09 |
|---|---|
| 231201 LeetCode 문제 풀이 (0) | 2023.12.01 |
| 23114 LeetCode 문제 풀이 (0) | 2023.11.14 |
| 231113 LeetCode 문제 풀이 (2) | 2023.11.13 |
| 231110 LeetCode 문제 풀이 (그래프, 인접 행렬) (0) | 2023.11.10 |



